Manual Testing
What is SDLC?
SDLC stands for (Software Development Life Cycle), it’s a standard or culture followed by all software industries.
SDLC is a step-by-step procedure for designing, developing, and testing to deliver a high-quality software product.
When to go for SDLC?
Whenever a person or software company wants to start a new project, they should follow (SDLC).
What happens if we don’t follow SDLC?
or
Why should we follow SDLC?
Chances are there we might not get the proper requirement document from the customer.
Chances are there we might not get to know how many engineers are required for a project.
Chances are there we might not get to know the operational cost required to work on a project.
Chances are there we might delay in releasing the software to the customer.
Stages of SDLC
REQUIREMENT COLLECTION
FEASIBILITY STUDY
DESIGN————1.HLD & 2.LLD
CODING
TESTING
INSTALLATION
MAINTAINANCE
Models of SDLC
Waterfall Model
Spiral Model
V-V Model or Verification & validation Model
Prototype Model
Derived Model
Hybrid Model
Agile Model
Types of Testing
Classification of Different Types of Testing
Testing is divided into two types –
Functional Testing
Non Functional Testing

What is Functional Testing?
Functional Testing is a type of software testing that validates the software system against the functional requirements/specifications. The purpose of Functional tests is to test each function of the software application, by providing appropriate input, verifying the output against the Functional requirements.
Functional testing mainly involves black box testing and it is not concerned about the source code of the application. This testing checks User Interface, APIs, Database, Security, Client/Server communication and other functionality of the Application Under Test. The testing can be done either manually or using automation.
Example of Functional Testing:
Let’s say you’re testing a login page of a website. The functional requirements of this login page may include:
The user should be able to enter their username and password.
The system should authenticate the user’s credentials and grant access if the credentials are correct.
The system should deny access if the user’s credentials are incorrect.
To test the functionality of this login page, you may perform the following functional tests:
Enter valid username and password and verify that the user is able to successfully login.
Enter invalid username and password and verify that the user is not able to login and an appropriate error message is displayed.
Verify that the login page displays correctly on different browsers and devices.
Verify that the password field is secure and does not display the entered password.
Verify that the “Forgot Password” feature works correctly and allows users to reset their passwords.
What is Non-Functional Testing?
Non-Functional Testing is defined as a type of Software testing to check non-functional aspects (performance, usability, reliability, etc) of a software application. It is designed to test the readiness of a system as per nonfunctional parameters which are never addressed by functional testing.
An excellent example of non-functional test would be to check how many people can simultaneously login into a software.
Example of Non functional Testing:
Let’s say you’re testing the performance of a website. The non-functional requirements of this website may include:
The website should be able to handle a certain number of concurrent users.
The website should load pages within a certain amount of time.
The website should be responsive and display correctly on different devices and screen sizes.
Accessible for users who are differently abled.
The website should be secure and protect user data.
Software Testing Techniques
Software test techniques refer to the methods used to test a software system. The most common software test techniques are
Black Box Testing Testing the behavior of applications bypassing all possible inputs and checking whether the application is working according to the CRS (Customer Requirement Specification) is called Black Box Testing.
a software testing technique where the internal workings or code structure of the system being tested are not known to the tester.
White Box Testing Testing each and every line of the source code according to the CRS (Customer Requirement Specification)
focuses on the software’s internal logic, structure, and coding. It provides testers with complete application knowledge, including access to source code and design documents, enabling them to inspect and verify the software’s inner workings, infrastructure, and integrations.
Grey Box Testing is a combination of black box and white box testing; involves some knowledge of the internal workings but focuses on functionality.
Levels of Testing in Software Testing
4 Levels of Testing
There are mainly four Levels of Testing in software testing :
Unit Testing : checks if software components are fulfilling functionalities or not.
Integration Testing : checks the data flow from one module to other modules.
System Testing : evaluates both functional and non-functional needs for the testing.
Acceptance Testing : checks the requirements of a specification or contract are met as per its delivery.

Each of these testing levels has a specific purpose. These testing level provide value to the software development lifecycle.
Each Testing Level Details
Unit testing:
A Unit is the smallest testable portion of system or application which can be compiled, liked, loaded, and executed. This kind of testing helps to test each module separately.
The aim is to test each part of the software by separating it. It checks that component are fulfilling functionalities or not. This kind of testing is performed by developers.
Integration testing
Integration means combining. For Example, In this testing phase, different software modules are combined and tested as a group to make sure that integrated system is ready for system testing.
Integrating testing checks the data flow from one module to other modules. This kind of testing is performed by testers.
System Testing
System testing is performed on a complete, integrated system. It allows checking system’s compliance as per the requirements. It tests the overall interaction of components. It involves load, performance, reliability and security testing.
System testing most often the final test to verify that the system meets the specification. It evaluates both functional and non-functional need for the testing.
Acceptance testing
Acceptance testing is a test conducted to find if the requirements of a specification or contract are met as per its delivery. Acceptance testing is basically done by the user or customer. However, other stockholders can be involved in this process.
Conclusion
A level of software testing is a process where every unit or component of a software/system is tested.
The primary goal of system testing is to evaluate the system’s compliance with the specified needs.
In Software Engineering, four main levels of testing are Unit Testing, Integration Testing, System Testing and Acceptance Testing.
What are the Software Testing Techniques and How are They Different from Testing Types?
Software test techniques refer to the methods used to test a software system. The most common software test techniques are
Black Box Testing is a software testing technique where the internal workings or code structure of the system being tested are not known to the tester.
White Box Testing focuses on the software’s internal logic, structure, and coding. It provides testers with complete application knowledge, including access to source code and design documents, enabling them to inspect and verify the software’s inner workings, infrastructure, and integrations.
Grey Box Testing is a combination of black box and white box testing; involves some knowledge of the internal workings but focuses on functionality.
These techniques are used to test a software system at different levels of detail, from a high-level view of the system’s functionality to a detailed view of its internal workings.
Read More: Differences between Black Box Testing and White Box Testing
While Software Testing Techniques, on the other hand, testing types refer to the different types of testing that can be performed within these test techniques.
For example, functional testing, regression testing, performance testing, security testing, usability testing, etc., are all different types of testing that can be performed within the black box, white box, or grey box test techniques.
Testing types are used to test different aspects of the software system and to ensure that it meets the stakeholders’ requirements.
Types of Functional Testing
Here are different types of Functional Testing:
Unit Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
1. Unit Testing
Unit testing is a software testing type in which individual units/components are tested in isolation from the rest of the system to ensure that they work as intended. A unit refers to the smallest testable part of a software application that performs a specific function or behavior. A unit can be a method, a function, a class, or even a module. They can be run in isolation or in groups. Unit tests are typically written by developers to check the correctness of their code and ensure that it meets the requirements and specifications.
Example of Unit Testing:
A developer has scripted a password input text field with its validation ar (8 characters long, must contain special characters.); makes a unit test to test out this one specific text field (has a test that only inputs 7 characters, no special characters, empty field)
Read More: Best Practices for Unit Testing
Advantages of Unit Testing
Early detection of Bugs
Simplifies Debugging Process
Encourages Code Reusability
Improves Code Quality
Enables Continuous Integration
Types of Unit Testing
a. Gorilla Testing
Gorilla testing is a software testing technique where the tester performs testing of a particular module or component of the software system rigorously and extensively to identify any issues or bugs that may arise. In other words, Gorilla testing focuses on testing a single module or component in depth to ensure that it can handle high loads and perform optimally under extreme conditions.
Example of Gorilla Testing
Testing a particular unit/module extensively to ensure that it handles heavy load.
Advantages of Gorilla Testing
Identify potential bottlenecks or weaknesses in a particular module
Capable of handling high loads
Helps identify issues or bugs that may be missed by other testing techniques
2. Integration Testing
Integration testing is a testing type in which different modules or components of a software application are tested together as a group to ensure that they work as intended and are integrated correctly. The main aim of integration tests is to identify issues that might come up when multiple components work together. It ensures that individual code units/ pieces can work as a whole cohesively.
Read More: Unit Test vs Integration Test
Integration testing can be further broken down to:
Component Integration Testing: This type of testing focuses on testing the interactions between individual components or modules.
System Integration Testing: This type of testing focuses on testing the interactions between different subsystems or layers of the software application.
End-to-End Integration Testing: This type of integration testing focuses on testing the interactions between the entire software application and any external systems it depends on.
Example of Integration Tests: A software application consists of a web-based front-end, a middleware layer that processes data, and a back-end database that stores data. Integration tests would verify if the data submitted in the front end is processed by the middleware and then stored by the backend database.
Advantages of Integration testing:
Early Detection of Issues
Improved Software Quality
Increased Confidence in the Software
Reduced Risk of Bugs in Production
Better Collaboration Among Team Members
More Accurate Estimation of Project Timelines
3. System Testing
System testing is a testing type that tests the entire software application as a whole and ensures that the software meets its functional and non-functional requirements. System testing is typically performed after integration testing. During system testing, testers evaluate the software application’s behavior in various scenarios and under different conditions, including normal and abnormal usage, to ensure that it can handle different situations effectively.

Example of System Testing
A software application consists of a web-based front-end, a middleware layer that processes data, and a back-end database that stores data. The system test for this scenario would involve the following steps:
The user accesses the front-end interface and submits an order, including item details and shipping information.
The middleware layer receives the order and processes it, including verifying that the order is valid and the inventory is available.
The middleware layer sends the order information to the back-end database, which stores the information and sends a confirmation message back to the middleware layer.
The middleware layer receives the confirmation message and sends a response back to the front-end indicating that the order has been successfully processed.
Advantages of System Testing
Identifies and resolves defects or issues that may have been missed during earlier stages of testing.
Evaluates the software application’s overall quality, including its reliability, maintainability, and scalability.
Increases user satisfaction
Reduces risk
Types of System Testing
a. End to End Testing
End-to-end testing is a testing methodology that tests the entire software system from start to finish, simulating a real-world user scenario. The goal of end-to-end testing is to ensure that all the components work together seamlessly and meet the desired business requirements. Most often people use the term system testing and end to end testing interchangeably. However both of them are different types of testing.
System testing is a type of testing that verifies the entire system or software application is working correctly as a whole. This type of testing includes testing all the modules, components, and integrations of the software system to ensure that they are working together correctly. The focus of system testing is to check the system’s behavior as a whole and verify that it meets the business requirements.
End-to-end testing, on the other hand, is a type of testing that verifies the entire software application from start to finish, including all the systems, components, and integrations involved in the application’s workflow. The focus of E2E testing is on the business processes and user scenarios to ensure that they are working correctly and meet the user requirements.
Example of End to End Testing
E-commerce transaction: End-to-end testing of an e-commerce website involves testing the entire user journey, from product selection to payment, shipping, and order confirmation.
Advantages of End to End testing
Allows you to test real world scenarios
Comprehensive testing
Improves quality
b. Monkey Testing
Monkey testing is a testing type where the tester tests in a random manner with random inputs to analyze if the application breaks. The objective of monkey testing is to verify if an application crashes by giving random input values. There are no special test cases written for monkey testing.
Also Read: Monkey Testing with WebdriverIO
Example of Monkey Testing
A tester randomly turning off the power or unplugs the system to test the application’s ability to recover from sudden power failures.
Advantages of Monkey Testing
Does not require extensive knowledge
Ensures reliability
Used to identify bugs that cannot be discovered through traditional methods
Cost Effective
Difference between Monkey Testing and Gorilla Testing: Monkey testing and gorilla testing are not the same, although they both involve sending random input data to the software system to observe its behavior. Monkey testing is focused on finding defects related to unexpected or invalid input, while gorilla testing is focused on thoroughly testing a specific feature or functionality of the software system.
c. Smoke Testing
Smoke testing is a testing type that is conducted to ensure that the basic and essential functionalities of an application or system are working as expected before moving on to more in-depth testing.
Example of Smoke Testing
Smoke testing for login will check whether the login screen is accessible and if the users can log in.
Advantages of Smoke Testing
Quick Feedback
Early detection of defects
Also Read: Sanity Testing vs Smoke Testing
4. Acceptance Testing
Acceptance Testing verifies whether a software application meets the specified acceptance criteria and is ready for deployment. It is usually performed by end-users or stakeholders to ensure that the software meets their requirements and is fit for purpose.
Acceptance Testing can be further divided into two types: User Acceptance Testing (UAT) and Business Acceptance Testing (BAT). User Acceptance Testing is performed by end-users to validate that the software meets their needs and is easy to use. Business Acceptance Testing is performed by stakeholders to ensure the alignment of business/functional requirements with the organization’s objectives.
Example of Acceptance Testing
Conducting tests to meet if an app meets the requirements of the user. For a banking app, acceptance testing would involve testing the app for login, account management, fund transfer, statement download, card payment etc.
Advantages of Acceptance Testing
Increased stakeholder engagement
Reduced Risk
Reduced costs
Types of Acceptance Testing
a. Alpha Testing
Alpha testing is a type of testing that is performed in-house by the development team or a small group of users. It is the first phase of testing that is conducted before the software is released to the public or external users. Alpha testing is a crucial step in the software development process as it helps to identify bugs, defects, and usability issues before the product is released.
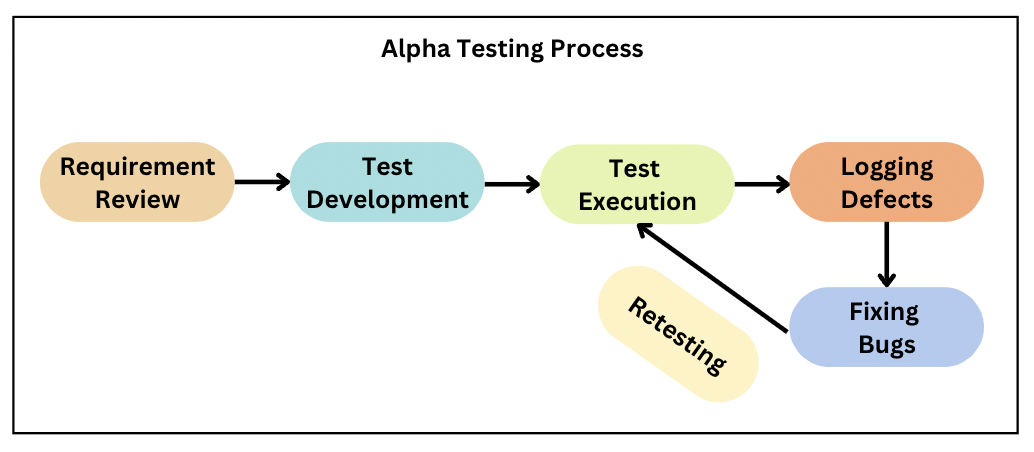
Example of Alpha Testing
A game development company is creating a new game. The development team performs alpha testing by testing the game’s performance, such as loading times, graphics, sound effects, and gameplay.
Advantages of Alpha Testing
Early detection of issues
Enhanced user experience
Feedback from internal users
b. Beta Testing
Beta testing is a type of testing that is performed by a group of external users who are not a part of the development team. The purpose of beta testing is to gather feedback from real users and to identify any issues that were not found during the alpha testing phase.
Example of Beta Testing
A software company is releasing a new feature of its product. The company invites a group of external users to beta test the product and provide feedback on any bugs, defects, or issues that were not found during the alpha testing phase.
Advantages of Beta Testing
Real-world feedback
Marketing and promotion
Enhanced user experience
c. User Acceptance Testing
User acceptance testing is a type of acceptance testing that is performed by the end-users of the software system. The focus of UAT is to validate the software system from a user’s perspective and to ensure that it meets their needs and requirements. UAT is typically performed at the end of the software development lifecycle.
Example of User Acceptance Testing
A company asks a batch of its customers to test the website and provide feedback on its functionality, usability, and overall user experience. Based on the feedback, it makes the necessary changes and improvements to the website.
Advantages of User Acceptance Testing
Reduced development costs
Improved customer satisfaction
d. Sanity Testing
Sanity testing is a testing type that is performed to quickly determine if a particular functionality or a small section of the software is working as expected after making minor changes. The main objective of sanity testing is to ensure the stability of the software system and to check whether the software is ready for more comprehensive testing.
Example of Sanity Testing
After fixing a bug that caused a crash in a mobile application, you can perform sanity testing by opening the app and ensuring that it does not crash anymore
Advantages of Sanity Testing
Quick and efficient
Saves time and effort
Cost-effective
Types of Non Functional Testing
Here are different types of Non Functional Testing:
Security Testing
Performance Testing
Usability Testing
Compatibility Testing
1. Security Testing
Security testing is a type of software testing that assesses the security of a software application. It helps to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the system and ensure that sensitive data is protected.
Examples of security testing include penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and authentication testing.
Advantages of Security Testing
Improved system security
Protection of sensitive data
Compliance with regulations
Types of Security Testing
Penetration testing: This involves attempting to exploit potential vulnerabilities in the software system by simulating an attack from a hacker or other malicious actor.
Fuzz testing: This involves sending many unexpected or malformed input data to the software system to identify potential vulnerabilities related to input validation and handling.
Access control testing: This involves testing the software system’s access control mechanisms inorder to make sure that the access to sensitive data is granted only authorized users.
2. Performance Testing
Performance testing is a type of software testing that assesses the performance and response time of a software application under different workloads. It helps to identify bottlenecks in the system and improve the performance of the application.
Examples of performance testing include load testing, stress testing, and volume testing.
Advantages of Performance Testing
Increased customer satisfaction
Better scalability
Improved user experience
Types of Performance Testing
a. Load Testing
Load testing is a type of performance testing that assesses the performance and response time of a software application under a specific workload. It helps to identify the maximum capacity of the system and ensure that it can handle the expected user load.
Examples of Load Testing
Simulating multiple users accessing a website at the same time or performing multiple transactions on a database.
Advantages of Load Testing
Improved system reliability
Better scalability
b. Stress Testing
Stress testing is a type of performance testing that assesses the performance and response time of a software application under extreme workloads. It helps to identify the system’s breaking point and ensure that it can handle unexpected workloads.
Examples of Stress Testing
Simulating thousands of users accessing a website simultaneously or performing millions of transactions on a database.
Advantages of Stress Testing
Improved system reliability
Better preparedness for real-world scenarios
Better scalability
c. Volume Testing
Volume testing is a type of testing that assesses the performance and response time of a software application under a specific volume of data. It helps to identify the system’s capacity to handle large volumes of data.
Examples of Volume Testing
Inserting large amounts of data into a database or generating large amounts of traffic to a website.
Advantages of Volume Testing
Improved system reliability
Better scalability
d. Scalability Testing
Scalability testing evaluates the software’s ability to handle increasing workload and scale up or down in response to changing user demands. It involves testing the software system under a range of different load conditions to determine how it performs and whether it can handle increasing levels of traffic, data, or transactions.
Examples of Scalability Testing
Testing a website by gradually increasing the number of simulated users accessing the website and tracking how the system responds to it.
Advantages of Scalability Testing
Optimize system performance
Better scalability
e. Endurance Testing
The goal of endurance testing is to identify how well a software system can handle a workload over an extended period of time without any degradation in performance or stability. It involves simulating a normal or average workload or traffic scenario over a period of a few weeks to months.
Examples of Endurance Testing
Testing a website for performance with normal or average user traffic over an extended period.
Advantages of Endurance Testing
Identifies long-term performance issues
Reduces downtime
Enhances user experience
3. Usability Testing
Usability testing is focused on evaluating the user interface and overall user experience of a software application or system. It involves testing the software with real users to assess its ease of use, learnability, efficiency, and overall user satisfaction.
Types of Usability Testing
a. Exploratory Testing
Exploratory Testing is a software testing type that is unscripted, meaning that the tester does not follow a pre-defined test plan or test case. Instead, the tester relies on their own expertise, intuition, and creativity to explore the software and find defects.
Example of Exploratory Testing
A tester testing for different actions, such as tapping different buttons, swiping screens, and inputting different types of data . The tester might look for crashes, freezes, errors, and unexpected behaviors throughout the exploration.
Advantages of End to End testing
Exploratory testing allows testers to be more flexible.
Exploratory testing can often be more time-efficient
Used to test real world scenarios
b. User interface Testing (UI Testing)
UI Testing (User interface testing) is a type of software testing that focuses on testing the graphical user interface (GUI) of an application. The purpose of user interface testing is to ensure that the application’s GUI is functioning correctly and meets the requirements and expectations of end-user
Examples of User Interface Testing
Identifying visual bugs in the layout, design, color scheme, font size, and placement of buttons.
Advantages of User Interface Testing
Identifying visual bugs
Reduced development costs
Increased Productivity
Increased Usability
c. Accessibility Testing
Accessibility testing is a type of testing that is focused on evaluating the accessibility of a software application or system for users with disabilities. It involves testing the software with assistive technologies, such as screen readers or voice recognition software, to make sure that differently abled users are able to access and use the software application effectively.
Examples of Accessibility Testing
Testing a website with a screen reader to ensure that the website is compatible with screen readers and its content is accessible via text-to-speech.
Advantages of Accessibility Testing
Improved User Experience
Better Credibility
Also Read: Quick Website Accessibility Testing Checklist
4. Compatibility Testing
Compatibility testing evaluates the compatibility of a software application or system with different hardware, software, operating systems, browsers, and other devices or components.

Also Read: Cross Browser Compatibility Testing beyond Chrome
Types of Compatibility Testing
a. Cross Browser Testing
Cross browser testing is a type of software testing that ensures a web application or website works correctly across multiple browsers, operating systems, and devices. It involves testing the website’s functionality, performance, and user interface on different web browsers such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, Safari, and Opera, among others.
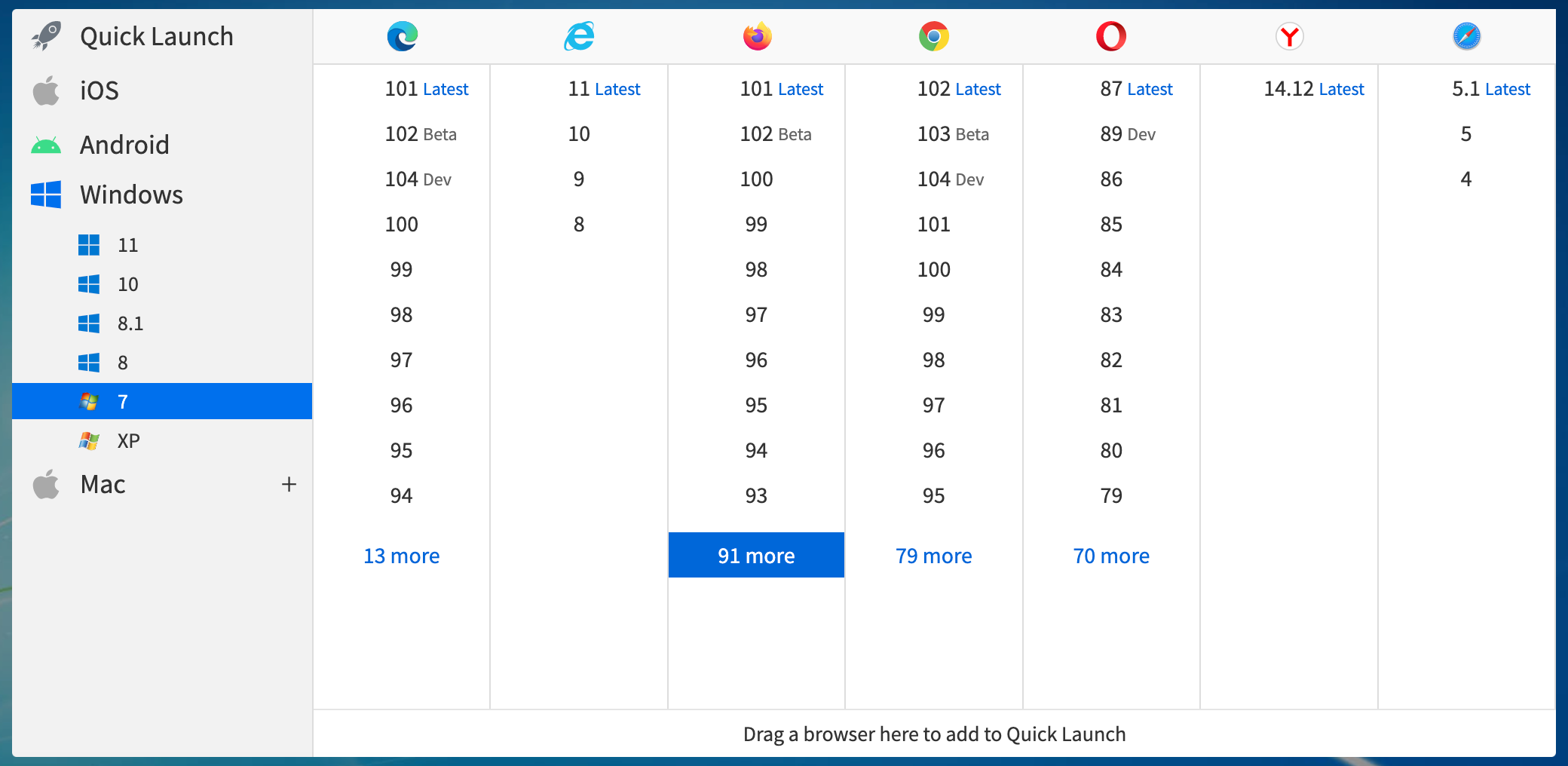
Examples of Cross Browser Testing
A tester testing on different versions of Google Chrome to identify issues that might arise in a particular version or a tester testing on different browsers to identify issues particular to a browser.
Read more: How to choose a Cross Browser Testing Tool
Advantages of Cross Browser Testing
Increased customer satisfaction
Enhanced brand reputation
Early detection of issues
Improved website traffic and conversion
b. Cross platform Testing
Cross platform testing is a testing type that ensures that an application or software system works correctly across different platforms, operating systems, and devices. It involves testing the application’s functionality, performance, and user interface on different platforms such as Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS, and others.
Examples of Cross Platform Testing
A software company is developing a new accounting software system. The company performs cross-platform testing to ensure that the software works correctly on different operating systems such as Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Advantages of Cross Platform Testing
Improved software quality
Competitive Advantage
Improved market reach
Other Types of Testing
Here are some other types of testing listed below:
Regression Testing: Regression Testing is a software testing type that ensures that changes or modifications to an existing software application do not introduce new defects or negatively impact existing functionality.
Recovery Testing: Recovery testing is a type of software testing that evaluates the system’s ability to recover from failures, errors, and other disruptions.
API Testing: API testing is the process of testing the functionality, reliability, performance, and security of an application programming interface (API). An API consists of protocols, routines, and tools for building software applications.
Active Testing: This type of testing involves executing test cases with a specific purpose and expected outcome.
Agile Testing: It is a software testing approach that follows the principles and rules of Agile software development.
Ad-hoc Testing: This type of testing is performed without any predefined test plan or test case.
Benchmark Testing: This type of testing involves comparing the performance of the software system against established benchmarks or industry standards.
Branch Testing: This type of testing is done to ensure that all the branches of the code are tested thoroughly.
Code-driven Testing: This type of testing involves writing test cases in the same programming language as the code being tested. It helps in finding defects at an early stage of development.
Context Driven Testing: Context-driven testing is a type of software testing used before launching in the market to test it on all the parameters, including performance, UI, speed, functionalities, and other aspects of the software to identify and fix bugs.
Dynamic Testing: This type of testing involves you have to give input and get output as per the expectation through executing a test case
Data Driven Testing: In this type of testing, testers use different data sets to validate the software system’s behavior under different conditions.
GUI Testing: This type of testing focuses on validating the graphical user interface of the software system. Testers verify that the user interface is intuitive and easy to use.
Localization Testing: This type of testing ensures that the software system can be easily adapted to different demographics. Language, currency etc are tested here.
Keyword-driven Testing: This type of testing involves using keywords to define the test cases. Testers use predefined keywords to create test scripts that are executed by an automated testing tool.
Parallel Testing: This type of testing involves executing the same test cases on multiple systems simultaneously. It helps in identifying performance issues and defects that are specific to certain configurations.
Path Testing: This type of testing involves testing all possible paths through the code to ensure that each path has been executed, and all the expected outcomes are met.
Retesting: Retesting is when a test is carried out again on a specific feature that was known to not be functional during the previous test in order to check for its functionality.
Static Testing: This type of testing involves analyzing the code and other artifacts without executing them. Testers review the code, documentation, and other artifacts to identify defects and potential issues.
Also Read: Static Testing vs Dynamic Testing
Manual Testing vs Automated Testing
It is essential to map out which test cases will be manually tested and which parts will be done via automated testing, irrespective of the testing type that you choose. Read this interesting article on manual vs. automated testing to understand the difference between the two.
| Criteria | Manual Testing | Automation Testing |
| Accuracy | Manual Testing shows lower accuracy due to the higher possibility of human errors. | Automation Testing depicts a higher accuracy due to computer-based testing eliminating the chances of errors. |
| Testing at Scale | Manual Testing needs time when testing is needed at a large scale. | Automation Testing easily performs testing at a large scale with the utmost efficiency. |
| Turnaround time | Manual Testing takes more time to complete a testing cycle, and thus the turnaround time is higher. | Automation Testing completes a testing cycle within record time; thus, the turnaround time is much lower. |
| Cost Efficiency | Manual Testing requires more cost as it involves hiring expert professionals. | Automation Testing saves costs incurred as once the software infrastructure is integrated; it works for a long time. |
| User Experience | Manual Testing ensures a high-end User Experience to the software’s end user, as it requires human observation and cognitive abilities. | Automation Testing cannot guarantee a good User Experience since the machine lacks human observation and cognitive abilities. |
| Areas of Specialization | To exhibit the best results, manual Testing should be used to perform Exploratory, Usability, and Ad-hoc Testing. | Automation Testing should be used to perform Regression Testing, Load Testing, Performance Testing, and Repeated Execution for best results. |
| User Skills | Users must be able to mimic user behavior and build test plans to cover all the scenarios. | Users must be highly skilled at programming and scripting to build test cases and automate as many scenarios as possible. |
Both manual and automation testing have their own advantages and disadvantages. It is essential to choose the appropriate testing approach based on the project’s requirements, time frame, budget, and complexity. Sometimes a combination of both manual and automation testing can be used to achieve the best results.

